This command technically walks through directories tree on the file system. It can be used to find directory and file matched with RegEx patterns.
General syntax for find command:
$ find [OPTIONS] [PATH...] [EXPRESSION]
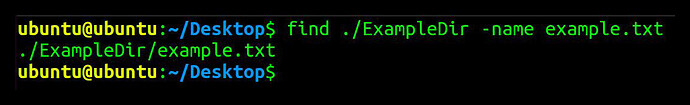
Search for specific file in a directory
find . /ExampleDir -name example.txt
With the -name parameter, this command will attempt to search for a example.txt within the ExampleDir directory; and if found, will return path to the file.
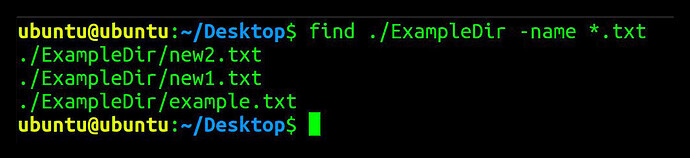
Find and list files of same extension
find . /dirname -name *.txt
This command will search, within the ExampleDir directory, all files ending with the extension .txt. If found, each result will be returned in a new line.
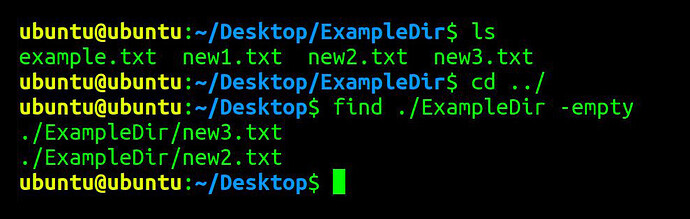
Find and list empty files and empty sub-directories
find . /ExampleDir -empty
This command, with the -empty parameter, will find and list all empty files and empty sub-folders inside the ExampleDir folder.
Definition of empty file being 0 bytes filesize, and empty folder being no files or files with 0 bytes.
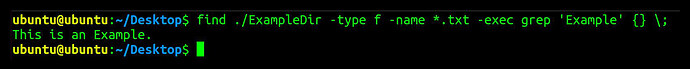
Find and list files that contain specific text
find . /ExampleDir - type f -name "*.txt" - exec grep 'Example' {} \;
This command searches for the word/string “Example” inside files with the extension .txt inside ExampleDir directory.
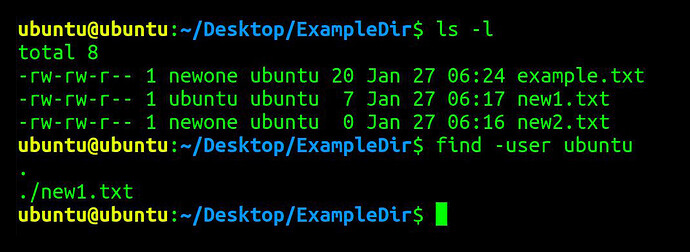
Find and list files and sub-directories own by specific user
find . /ExampleDir -user ubuntu
This command, with the -user parameter, will find files and sub-directories owned by Ubuntu user in ExampleDir directory. If found, the filename(s) will be returned.
In the following sample ls -l result:
-rw-rw-r-- 1 newone ubuntu 20 Jan 27 06:24 example.txt
newone represents group name, and ubuntu is the user.
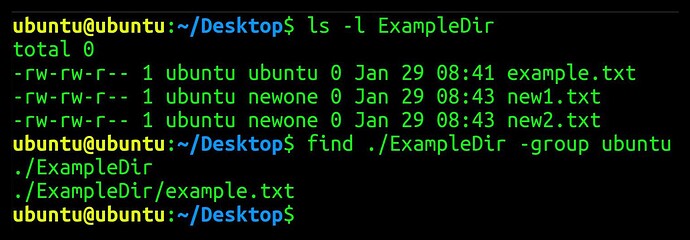
Find and list files and sub-directories own by specific group
find . /ExampleDir -group ubuntu
This command, with the -group paramter, will find all files and sub-directories owned by Ubuntu group in ExampleDir directory. If found, the filename(s) will be returned.
Happy learning!
 !
!