First things first, before we jump right in, let’s understand a few points:
- By default, Windows does not log the IP address of a failed RDP connection
- Third party tools are not required to get the IP address
- Small changes to our environment are required to get the IP address
- NLA must also be disabled.
So what is NLA exactly? NLA was implemented by Microsoft as a way to increase the security of RDP. So if we disable NLA, aren’t we weakening the security of our system? Not really, it won’t pose a significant risk and here’s why. RDP uses strong encryption by default and NLA only reduces the risk of denial-of-service attacks. All that NLA is doing is reducing the amount of resources that are used at the initial stages of an RDP connection. So NLA is a denial-of-service protection, not an encryption or authentication solution. To better understand the differences here are before and after pictures with NLA enabled and NLA disabled.
NLA enabled
NLA disabled
As you can see, NLA is just hiding the login prompt. With NLA enabled, we never see the desktop logon prompt and not sending that information down the wire reduces resources and helps to prevent denial-of-service attacks. With NLA disabled, we can see the desktop logon prompt. To read more about NLA, reference this article.
Instructions:
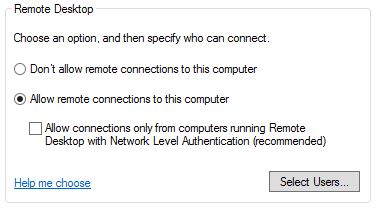
- Disable NLA on the server. This step must be completed first, or you’ll break RDP when we disable NTLM. Right click computer > properties > uncheck the box below ‘Allow remote connections to this computer’.
- Disable NTLM. Using group policy or local security manager, navigate to Local Policies > Security Options.
 ’
’
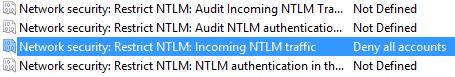
- Locate the below entry for ‘Network security: Restrict NTLM: Incoming NTLM traffic’. Set to ‘Deny all accounts’.
- Create a Windows firewall rule for our script. I am calling mine ‘My BlackList’ Call yours whatever you’d like, just make a note of it as we’ll need it later on.
Using Windows Firewall with Advanced Settings, select Inbound Rules > New Rule.
- Select Program > Next.
- All programs > Next.
-
Allow the connection . THIS IS IMPORTANT. Do NOT select ‘Block the connection’ or you’ll kick everyone off the server, so allow the connection and we’ll block it later > Next.
-
Check the boxes that match your environment > Next.
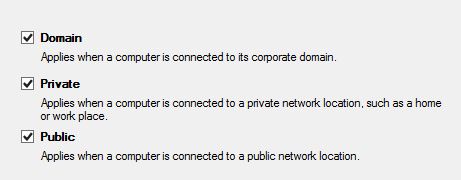
- Name the rule > Finish.
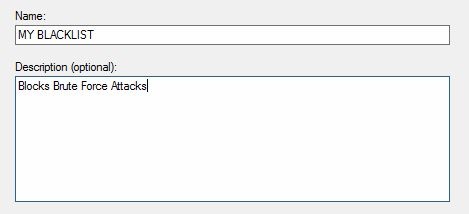
- Open the newly created rule to finish a few parameters.
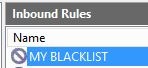
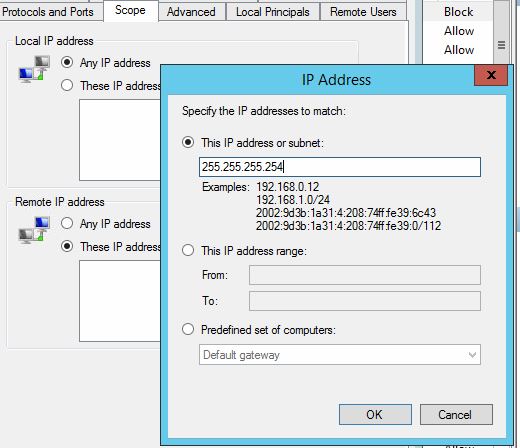
- Select the Scope tab and add 255.255.255.254. This is a placeholder IP so the rule won’t block everyone!
- With a placeholder IP address added, we can now block the connection. Using the General tab select ‘Block the connection’ > OK

- Windows firewall is now configured, so we can now configure the Powershell script. Open the script and find these two lines. Update the bold text with your information.
- $logfile = " C:\support\blocked.txt "
- $ar = $fw.rules | where {$_.name -eq ’ MY BLACKLIST’ }
Download your copy of the powershell script
-
Save the script. Next, we’ll create a schedule task, so it runs automatically.
-
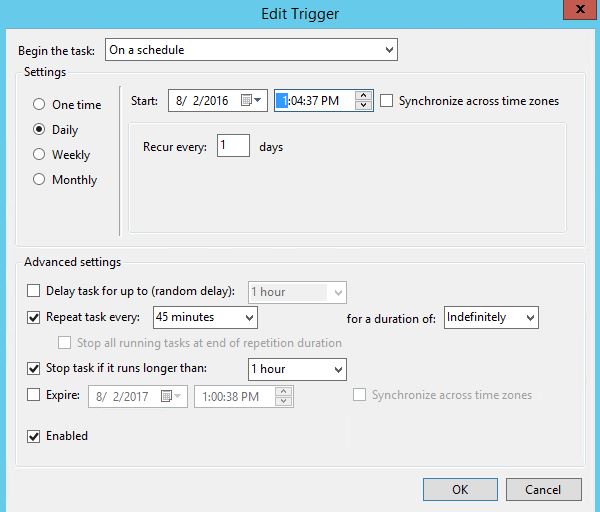
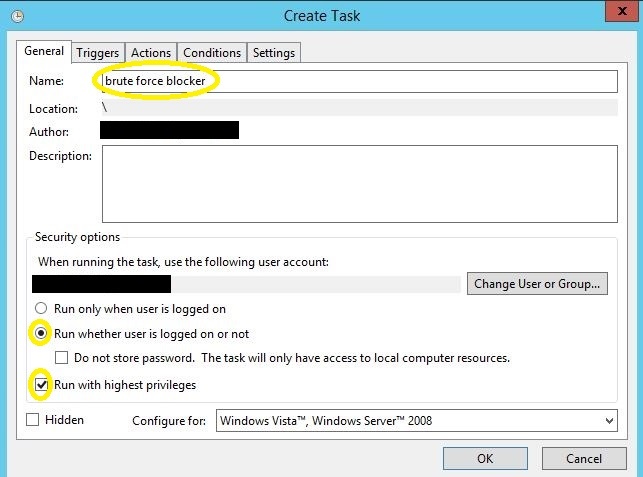
Open task manager and select ‘Create New Task’. Give it a proper name and ensure that ‘Run whether user is logged on or not’ is selected and that ‘run with highest privileges’ is selected. Sensitive information has been removed from this graphic.
- Define the Triggers tab. Configure the ‘Repeat task every’ to a value that is less than your account lockout duration. For example, if the account lockout duration is 60 minutes, then configure the task for every 45 minutes.
- Next is the Actions tab. Browse to the location of the script and append the following to the ‘Program/script:’ section: exe –file
- The entire string will look like this:
- powershell.exe -file C:\support\scripts\BruteForceBlocker.ps1
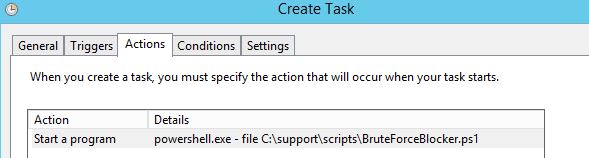
-
The rest of the settings can remain at the default settings.
-
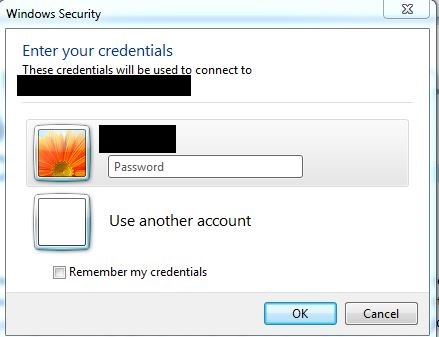
Click OK and enter the username and password of the user account. *Note the user account will require ‘run scheduled task/batch file permissions’. Sensitive information removed from screenshot.
- Click yes at the next prompt.
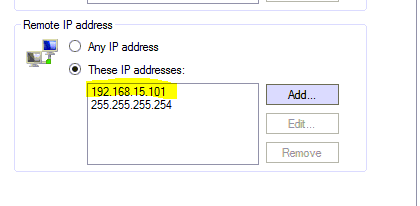
21 . Next, you’ll need to purposefully fail a login 10 times. Once that happens the computer will no longer be able to connect via RDP and you’ll see the IP address blocked in the ‘MY BlackList’. For illustration purposes, I am showing an internal IP address in the picture, but it will block external IP addresses as well.  :
:
That’s all there is to it. Now you have an automated brute force attack blocker that doesn’t require any third-party tools.
Source: watchpointdata