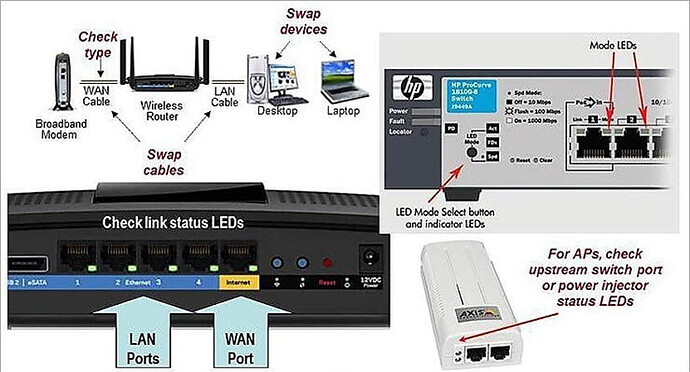
When we run a network or while working in any system there are always chances of failure in the smooth operation owing to technical, physical or any other faults.
For uninterrupted running of the system, we need to resolve the raised issues as soon as possible and for this, we need to detect the cause of the problem first and then fix it.
Thus the process of detection, minimization and resolving the faults that arise in the network while performing the various day to day activities is known as troubleshooting.
Here we will explore the different kinds of troubleshooting steps and the tools we use for fault detection and closure of the same.
Network Troubleshooting
In this tutorial, we are only concerned about the computer networking fault diagnosis and rectification.
Based on the type of issue, we will discuss its troubleshooting steps and tips.
Basic Network Problems
- Cable Problem : The cable which is used to connect two devices can get faulty, shortened or can be physically damaged.
- Connectivity Problem : The port or interface on which the device is connected or configured can be physically down or faulty due to which the source host will not be able to communicate with the destination host.
- Configuration Issue : Due to a wrong configuration, looping the IP, routing problem and other configuration issues, network fault may arise and the services will get affected.
- Software Issue : Owing to software compatibility issues and version mismatch, the transmission of IP data packets between the source and destination is interrupted.
- Traffic overload: If the link is over utilized then the capacity or traffic on a device is more than the carrying capacity of it and due to overload condition the device will start behaving abnormally.
- Network IP issue: Due to improper configuration of IP addresses and subnet mask and routing IP to the next hop, the source will not be able to reach the destination IP through the network.
Network Troubleshooting Flowchart
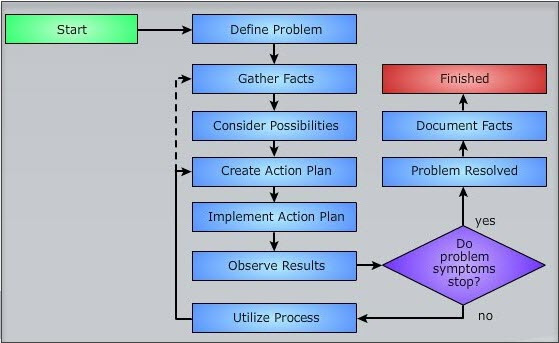
Steps Involved In Network Diagnostics
Here steps to troubleshoot and diagnose various network problems like IP, connectivity, wireless connection, etc.
Troubleshooting IP Problems
In the TCP/IP protocol suite, if we are not able to reach at the destination IP address and not able to find the route to reach the next hop at any point in the network, then we will use PING and TRACEROUTE tools for troubleshooting the cause and location of the issue.
The generic steps to troubleshoot the IP related issues in the network include:
- Firstly locate the pair of devices between the source and the destination host between which the connectivity issue has occurred.
- Once you locate the devices using the tools, the fault can be due to a physical connectivity issue. Thus check the physical connections all over the path.
- There can be a fault in the LAN connectivity as well if you are working in a LAN network. So check the LAN connections. The local port can be faulty or down due to which the source cannot be able to reach the destination IP.
- One of the reasons of the fault can be the router connectivity issue while traveling through various paths to reach the destination. Hence check that if the router is defined properly at each of the intermediate hops.
- Check the configuration settings.
Troubleshooting Local Connectivity Issues
Once on the broad level, if you find that there is an issue in the LAN connectivity, then in order to locate the root cause and to resolve it, you should follow the below steps:
- If the destination and the source are of the identical subnet mask, then try to ping the destination IP.
- Else, if the destination is of some other subnet mask then try to ping the gateway IP address of the router.
- Now, if both the ping fails, then first check that in the configuration settings, if both the subnet mask and route to be followed to reach the destination are defined properly in the routing table or not?
- Once you are done with the configuration part and found everything OK, then check if your source host is able to ping some another hop in the LAN network other than the destination host or route to that?
- If you are not able to ping to another device then there can be many reasons for this. It may even be a configuration issue, a physical connectivity issue, and repetitive IP address entry issue.
Correcting the Repetitive IP address Entry Issue
For rectifying the duplicate entry of an IP issue, disconnect the doubtful device from the LAN and also make the interface on which the device was connected shut down.
Now ping the device from some another device of the same subnet or LAN network. If the ping is OK, then it indicates that the IP is being used by some other device as well on the network. From the ARP table of the device, find out its MAC address and modify the IP address according to planning.
But if the problem persists still, then there will be a physical connectivity or configuration issue in it.
Troubleshooting Physical Connectivity Issues
The list of faults that come under this category are:
- Improper connection of cables
- Router, switch or hub port is faulty or down.
- Traffic overload on the link or particular interface.
- Configuration issue at layer-1.
Let’s take a look at the above in detail.
#1) Checking Cable connectivity Issue : The cables are used for connections, based on the type of connectivity. Like, for connectivity between a router and a computer the crossover pair of the cable is used. Thus make sure that the suggested and suitable cable is used to make a physical connection between any two devices .
If connections are found ok, then maybe the cable is faulty, so check the connectivity by replacing the existing cable with a newer one. Still, if the problem persists, then check the port or interface on which the link is terminated. There is a possibility for the port to be faulty.
2) Port Faulty Scenario : Check that the port or interface on which the link is established is not shut down. Verify the duplex mode and speed as well. If the port is up and still the problem persists, then there are indicator lights that are present on each of the device to show the running status of the port.
From the indicator lights, check if the port is physically radiating or down. If the port is physically malfunctioning then it will appear by light status. In this situation, configure the link on some other free port or interface.
#3) Traffic overload : If there is more traffic than the carrying capacity at a link or interface then at some point it will start behaving abnormally. Thus verify these criteria to ensure smooth running.
#4) Configuration Issue : Check the router configuration on the interface by show ip interface and show running-config commands.
Troubleshooting Routing Problems
When we route the data packets in the network, then the chances for occurrences of fault are usual. Thus depending on the type of fault, we will prepare our plan for resolving the faults.
The kind of fault that occurs between the source and destination hosts while floating data packets in a network are listed below:
- The route is not defined in the router between the source and destination.
- A wrong Routing protocol is used to find out the route to the next hop or destination.
- Software related fault at the router.
- Any filter or firewall may be barring the entry of data packets to the destination node.
- There may be configuration faults that arise at the source router end.
How to proceed for resolution:
- To find out the resolution, the first step is to locate the hop between the source and the destination where the problem has occurred.
- The process verifies the IP connectivity and routing protocols connectivity at each hop starting from the source host towards the destination one.
- We can also use the traceroute tool to locate the hop where the problem has arised. But this is not helpful in all the cases. Hence, it is better if we proceed with the first one.
- Once we locate the problematic hop, then login to that router via telnet and then try to ping the source and destination host.
- If the ping is not successful, then verify the routing table for routes between the source and destination. If routes are not defined then configure the IP routes with the subnet mask and default route in the router.
- In condition, if the ping responses with only a few percentages of success, then there may be multiple paths that are defined to reach the destination. But out of multiple paths, one is failing to reach the destination. The cause for this is that a routing loop can occur in the path. To rectify this, trace the looping hop, and correct the configuration.
- After rectification of the above steps, if still, the problem persists, then check the routing protocol used, and change the protocol in accordance with the network.
- The configuration issues at a particular router can be checked using a command like show ip interface for interface related faults, show ip access-group for finding out ant firewall or filter is configured in the network and you can check what is allowed to pass through it, show version for uptime and show running-config for the overall configuration.
Troubleshooting Upper-layer Faults
After checking the physical connectivity, Local connectivity, IP connectivity, and Routing issues, if you are still not finding a resolution for the fault, then there is a possibility for the fault to be the in transport and application layer protocol.
A fault can arise due to the following reasons:
- The data connection is down.
- A packet filter or firewall is blocking the incoming or outgoing traffic.
- Particular service on the server is down.
- There can be an authentication and access issue between the client and the server host.
- Software incompatibility or version mismatch issues between the source and the destination host.
Depending upon the category of fault, we take the rectification steps.
- In the condition of firewall barring the traffic to flow through the network, we look out for a way to move the source host in the network in such a way in which the firewalls can be avoided or bypassed.
- For service down issues, take measures to make it up, or align another server to deliver the service.
- For the authentication process issue, we can deploy checks with the help of the software where the authentication is failing, and then based on the results you can rectify the issue.
- For version mismatch and compatibility issue, upgrade your system so that both will be compatible with each other.
Troubleshooting Wireless Network Connection Issue
#1) Whenever you connect your Tablet, mobile phone or Laptop with the WI-FI device, and if you are not able to connect then check all the LAN or WAN cable connections.
The Ethernet cable should be connected tightly and check the light status on the device. If it is not green then the cable or port may be faulty. Thus change the port and cable connections with a newer one.
2) After verification of all of the above points, if the connection is still not through, then verify the WI-FI network adaptor settings.
For windows laptop or PC, go to control panel, select the network connections option and check what is the status on the wireless network adaptor? It should be enabled. If it is not enabled then click on the enable key and mark the status as enabled.
Also, check if the airplane mode on a laptop or PC is disabled. If it is enabled, then it will not allow connecting with a wireless network.
Network Adaptor Settings
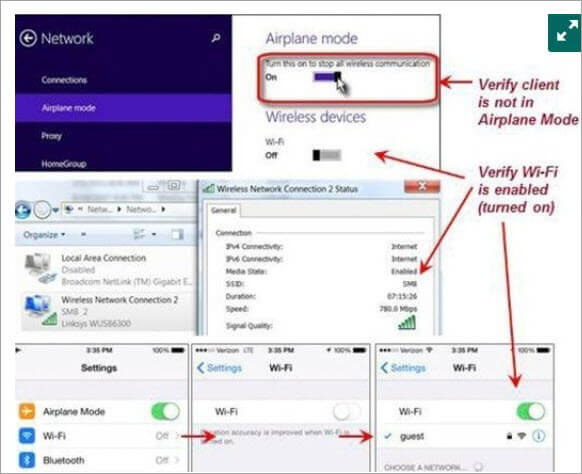
#3) After checking all the above settings, if the status is still not connected then check the wireless access point and SSID settings. After correction of the desired settings, the status will change from not connected to acquiring network address to connected. At this point, the client also allocates the IP address to the requesting device.
Network Connection Settings

#4) If still, the problem persists, then click on the diagnose option from the wireless network connection status menu to find out the cause.
#5) After performing all the above troubleshooting steps, if you are not able to connect to the network still, then there may be other reasons like some firewall or packet filter is barring you for using the network, and there could be a problem with the authentication protocol used etc.
#6) To resolve these issues, reconfigure all the network settings and verify the IP reachability by using PING.
These are the basic troubleshooting steps. If you are still not able to connect to the network, then you can restart your system and then try to connect and consult with some network settings expert.
Network Troubleshooting Tools
There are various tools that are used for checking the IP reachability issues and to locate where the packet is lost while communicating with the destination host. These tools make troubleshooting easier and minimize the time for restoration.
Some of the popular tools are mentioned below:
#1) SolarWinds Engineer’s Toolset
SolarWinds provides a network software, Engineer’s Toolset that contains over 60 tools.
With the help of these tools, you will be able to automate network discovery. For automated network discovery, it has a set of tools like Port Scanner, Switch Port Mapper, SNMP sweep, IP Network Browser, etc.
This software has powerful diagnostic capabilities. It will perform real-time monitoring and alerting. It provides the features of IP address & DHCP scope monitoring, Configuration & log management, and enhanced network security.
Engineer’s Toolset can be integrated with SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor. The tool will help you to perform network stress tests with WAN Killer. According to your specifications, it will generate random traffic and will allow you to adjust packet size, bandwidth, and percentage of bandwidth.
SolarWinds offers a fully functional free trial for 14 days. Per seat license of Engineer’s Toolset will cost you $1495.
=> Download SolarWinds Engineer’s Toolset For Free
2) Ping
By using IP ICMP echo request and echo reply messages, the PING tool verifies the reachability to the destination host at the remote end.
It contains two messages, first is, if the data packet is competent to send and receive the messages from the destination IP address and the second is the RTT time for the process (RTT means round trip time and is calculated in milliseconds).
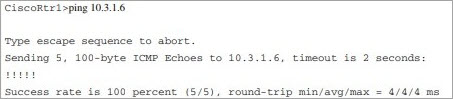
The exclamation shows that ping is successful. If the ping returns saying the destination is unreachable then there are many reasons for this. To find out the cause, we will go for the next tool.
#3) Trace Route
It sends the ICMP echo request messages with a step by step increase in the IP TTL (time to live) values.
The starting value is 1. It sends the data packet in a forward direction and each hop decreases the TTL value by 1 while routing the data and rejects the packet whose TTL value is zero by responding that the message ICMP time has exceeded.
Now again the source host sends the data packet, but this time with a TTL value of 2. In this way, the process will keep going until the packet has arrived at the destination and then the destination host reverts with ICMP echo reply messages.
With the help of traceroute, the router will keep a record of which route is followed by the packets to reach the destination and calculates the latency and other parameters as well.
#4) Protocol Analyzer
It is an advanced tool for finding out the network issues.
It is the software that intercepts and records the data packet flow between the source and the destination. Like, if the system is running slow then it can check for the latency issues and other networking problems which will help in diagnosing the root cause.
Tips For Network Troubleshooting
Some Tips include:
- Always use a high-level password to protect your network devices such as routers, switches and database servers as they store crucial data within themselves.
- Don’t share your router login user ID and password with anyone in the organization or outside the organization.
- Properly log-out from the system once your job is done.
- Keep verifying your configuration by show running-config command.
- For assigning IP addresses and subnet mask to the devices for a network, always perform the IP planning first and then make a diagram of the connectivity of devices that you are using in the network.
- It is better if you use the routers or servers in the master-slave mode so that in the worst case if one goes down then the other will take up the load and your network will be kept alive.
- Avoid overloading your device with high traffic.
Conclusion
The different kinds of fault categories that we counter within the networking systems is explained here in this tutorial.
We came to know that an issue can occur from the bottom layer to the top layer of the TCP/IP model and can be due to a physical connectivity issue, LAN issue, IP related issue or any routing related faults.
Based on the category of the issue, we take measures to locate and rectify them. Only the generic and basic troubleshooting steps of the networking system are explained. As it is a very vast topic, several other kinds of faults and newer faults can arise in any network at any time.
But as a beginner, it is important to understand the above-defined troubleshooting steps for ruling out the issue at the ground level.
enjoy the article folks ![]()