Table of contents
SQL Injection
SQL Injection threats
SQLI : Conclusion
SQL Injection Attacks
How Web Applications Work
Server-side Technologies
HTTP Post Request
SQL Injection Detection
SQL Injection Attack Characters
Testing for SQL Injection
Types of SQL Injection
Blind SQL Injection
Blind SQL Injection - Extract Database User
Blind SQL Injection - Extract Database Name
Blind SQL Injection - Extract Table Column Name
Blind SQL Injection - Extract Data from ROWS
SQL Injection Methodology
Advanced SQL Injection
Bypass Website Logins Using SQL Injection
MD5 Hash Password
Features of different DBMS
SQL Injection Tools
Recommended Tools
Other Tools
Evasion Technique
Evading IDSs
How to Defend Against SQL Injection Attacks
Word of Advice
Final Words
SQL Injection Detection Tools
1. SQL Injection
SQL injection is a type of web application vulnerability where an attacker can manipulate and submit a SQL command to retrieve the database information. This type of attack mostly occurs when a web application executes by using the user-provided data without validating or encoding it. It can give access to sensitive information such as social security numbers, credit card numbers, or other financial data to the attacker and allows an attacker to create, read, update, alter, or delete data stored in the backend database. It is a flaw in web applications and not a database or web server issue. Most programmers are still not aware of this threat.
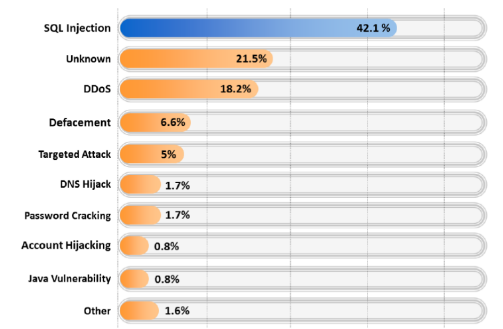
Fig 1.1: A recent study shows, above 40% of web attacks are still based on SQLI.
1.1 SQL Injection threats
Spoofing identity: Identity spoofing is a method followed by attackers. Here people are deceived into believing that a particular email or website has originated from the source which actually is not true.
Changing prices: One more of problem related to SQL injection is it can be used to modify data. Here the attackers enter into an online shopping portal and change the prices of product and then purchase the products at cheaper rates.
Tamper with database records: The main data is completely damaged with data alteration; there is even the possibility of completely replacing the data or even deleting the data.
Escalation of privileges: Once the system is hacked, the attacker seeks the high privileges used by administrative members and gains complete access to the system as well as the network.
Denial-of-service on the sewer: Denial-of-service on the server is an attack where users aren’t able to access the system. More and more requests are sent to the sewer, which can’t handle them. This results in a temporary halt in the services of the server.
Complete disclosure of all the data on the system: Once the network is hacked the crucial and highly confidential data like credit card numbers, employee details, financial records, etc. are disclosed.
Destruction of data: The attacker, after gaining complete control over the system, completely destroys the data, resulting in huge losses for the company.
Voiding system’s critical transaction: An attacker can operate the system and can halt all the crucial transactions performed by the system.
Modifying the records: Attackers can modify the records of the company, which proves to be a major setback for the company’s database management system.
1.2 SQLI : Conclusion
Structured Query Language (SQL) is basically a textual language that enables interaction with a database server. SQL commands such as INSERT, RETRIEVE, UPDATE, and DELETE are used to perform operations on the database. Programmers use these commands to manipulate data in the database server. SQL injection is defined as a technique that takes advantage of non-validated input vulnerabilities and injects SQL commands through a web application that are executed in a back-end database. Programmers use sequential SQL commands with client-supplied parameters making it easier for attackers to inject commands. Attackers can easily execute random SQL queries on the database server through a web application. Attackers use this technique to either gain unauthorized access to a database or to retrieve information directly from the database.
2. SQL Injection Attacks
On the basis of application used and the way it processes user supplied data, SQL injection can be used to implement the attacks mentioned below:
Authentication bypass : Here the attacker could enter into the network without providing any authentic user name or password and could gain access over the network. he or she gets the highest privilege in the network.
Information disclosure : After the unauthorized entry into the network, the attacjer gets access to sensitive data stored in the database.
Compromised data integrity : The attacker changes the main content of the website and also enters malicious content into it.
Compromiused availibility of data : The attacker uses this type of attack to delete the data related to audit information or any other crucial database information.
Remote code execution : An attacker could modify, delete, or create data or even can create new accounts with full user rights on the server that shares files and folders. It allows an attacker to compromise the host operating system.
2.1 How Web Applications Work
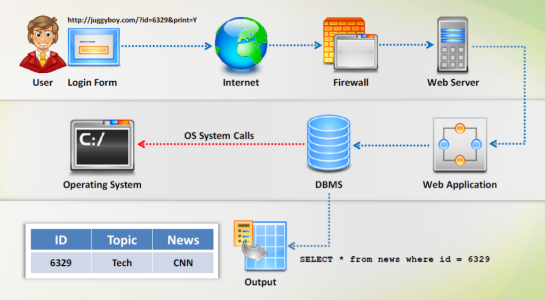
A web application is a software program accessed by users over a network through a web browser. Web applications can be accessed only through a web browser (Internet Explorer, Mozilla Firefox, etc.). Users can access the application from any computer of a network. Based on web applications, web browsers also differ to some extent. Overall response time and speed is dependent on connection speed.
Step 1: The user requests through the web browser from the Internet to the web server.
Step 2: The Web Server accepts the request and forwards the request sent by the user to the applicable web application server.
Step 3: The web application server performs the requested task.
Step 4: The web applications accesses the entire database available and responds to the web server.
Step 5: The web server responds back to the user as the transaction is complete.
Step 6: Finally the information that the user requested appears on the monitor of the user.
2.2 Server-side Technologies
This technology is used on the server side for client/server technology. For achieving business success, not only information is important, but we also need speed and efficiency. Server-side technology helps us to smoothly access, deliver, store, and restore information. Various server-side technologies include: ASP, ASP.Net, Cold Fusion, JSP, PHP, Python, and Ruby on Rails. Server side technologies like ASP.NET and SQL can be easily exploited by using SQL injections.
Powerful server-side technologies like ASP.NET and database servers allow developers to create dynamic, data-driven websites with incredible ease.
All relational databases, SQL Server, Oracle, IBM DB2, and MySQL, are susceptible to SQL injection attacks.
SQL injection attacks do not exploit a specific software vulnerability; instead they target websites that do not follow secure coding practices for accessing and manipulating data stored in a relational database.
The power of ASP.NET and SQL can easily be exploited by attackers using SQL injection attacks.
2.3 HTTP Post Request
An HTTP POST request creates a way of passing larger sets of data to the server. The HTTP POST requests are ideal for communicating with an XML web service. These methods are designed for data submission and retrieval on a web server.
When a user provides information and clicks Submit, the browser submits a string to the web server that contains the user’s credentials. This string is visible in the body of the HTTP or HTTPS POST request as:
select * from Users where (username = ‘bart‘ and password = ‘simpson’ Username: Password:
3. SQL Injection Detection
The following are the various steps to be followed to identify SQL injections.
Step 1: Check if the web application connects to a Database Server in order to access some data.
Step 2: List all input fields, hidden fields, and post requests whose values could be used in crafting a SQL query.
Step 3: Attempt to inject codes into the input fields to generate an error.
Step 4: Try to insert a string value where a number is expected in the input field.
Step 5: The UNION operator is used in SQL injections tojoin a query to the original query.
Step 6: Detailed error messages provide a wealth of information to an attacker in order to execute SQL injection.
4. SQL Injection Attack Characters
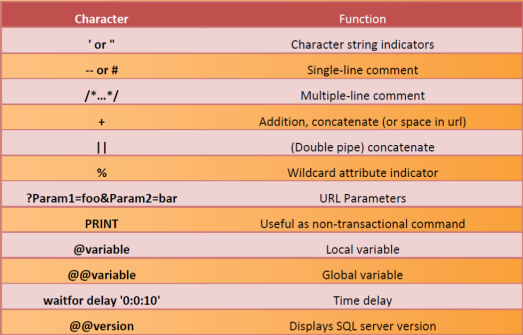
5. Testing for SQL Injection
SQL injection can be detected with the help of the following additional methods:
Function Testing: This testing falls within the scope of black box testing, and as such, should require no knowledge of the inner design of the code or logic.
In black box testing, the pen tester doesn’t need to possess any knowledge about the network or the system to be tested. The first job of the tester is to find out the location and system infrastructure. The tester tries to identify the vulnerabilities of web applications from the attacker’s perspective. Use special characters, white space, SQL keywords, oversized requests, etc. to determine the various conditions ofthe web application. The following are the various issues related to SQL injection black box penetration testing:
Detecting SQL Injection Issues
Send single quotes as the input data to catch instances where the user input is not sanitized. Send double quotes as the input data to catch instances where the user is not sanitized.
Detecting Input Sanitization
Use the right square bracket (the ] character) as the input data to catch instances where the user input is used as part of a SQL identifier without any input sanitization.
Detecting SQL Modification
Send long strings of single quote characters (or right square brackets or double quotes). These max out the return values from REPLACE and QUOTENAME functions and might truncate the command variable used to hold the SQL statement.
Detecting Truncation Issues
Send long strings of junk data, just as you would send strings to detect buffer overruns. This action might throw SQL errors on the page.
Fuzzing Testing: Fuzzy testing is a SQL injection testing technique used to discover coding errors by inputting a massive amount of data to crash the web application.
Static/Dynamic Testing : Static/dynamic testing is the manual analysis of the web application source code.
6. Types of SQL Injection
The following are the various types of SQL injection:
Blind SQL Injection Where ever there is web application vulnerability, blind SQL injection can be used either to access the sensitive data or to destroy the data. The attacker can steal the data by asking a series of true or false questions through SQL statements.
Simple SQL Injection A simple SQL injection script builds a SQL query by concatenating hard-coded strings together with a string entered by the user. Simple SQL injection is again divided into two types.
UNION SQL Injection : UNION SQL injection is used when the user uses the UNION command. The attacker checks for the vulnerability by adding a tick to the end of a ".php? id=“ file.
SQL Injection Error Based : The attacker makes use of the database-level error messages disclosed by an application. This is very useful to build a vulnerability exploit request.
7. What Is Blind SQL Injection?
Blind SQL injection is used when a web application is vulnerable to SQL injection. In many aspects, SQL injection and blind injection are same, but there are slight differences. SQL injection depends on error messages but blind injections are not dependent on error messages. Where ever there is web application vulnerability, blind SQL injection can be used to either access the sensitive data or to destroy the data. Attackers can steal the data by asking a series of true or false questions through SQL statements. Results of the injection are not visible to the attacker. This is also more time consuming because every time a new bit is recovered, then a new statement has to be generated.
7.1 Blind SQL Injection - Extract Database User
In the blind SQL injection method, the attacker can extract the database user name. The attacker can probe yes/no questions from the database server to extract information from it. To find the first letter of a user name with a binary search, it takes 7 requests and for 8 char long name it takes 56 requests.
7.2 Blind SQL Injection - Extract Database Name
In the blind SQL injection method, the attacker can extract the database name using the time-based blind SQL injection method. Here, the attacker can brute force the database name by using time before the execution of the query and set the time after query execution; then he or she can assess from the result that if the time lapse is 10 seconds, then the name can be ’A’; otherwise, if it took 2 seconds, then it can’t be ‘A’.
7.3 Blind SQL Injection - Extract Table Column Name
In the blind SQL injection method, the attacker can extract the column names using brute force methods or tools using which he or she can check for the first table column name and second table column name.
7.4 Blind SQL Injection - Extract Data from ROWS
In the blind SQL injection method, the attacker can extract the data from the rows using the command with the “IF” keyword and check if the first character of the word in the first column and row match the character by guessing.
8. SQL injection methodology
The following are the various stages of SQL injection methodology:
Information gathering: The attacker first gathers all the required information he or she needs before the SQL injection attack.
SQL injection vulnerability detection: Usually the attacker’s job is to identify the vulnerability of the system so that he or she can exploit the vulnerability to launch attacks.
Launch SQL injection attack: Where ever there is weak authentication, that will be the main source for the attacker to enter into the network and finally by exploiting the authentication rules, the attacker injects the malicious code of SQL injection.
Extract the data: The attacker gets access to the network as a privileged user and will be able to extract the sensitive data from the network.
Interact with the operating system: Once he or she gains access, the attacker tries to escalate his or her privileges so that he or she can interact with the operating system.
Compromise the system: The attacker can modify, delete the data, or create new accounts as a privileged user depending on the purpose of the attack. Again, from there, the attacker can log into the other associated networks. He or She can then use malwares for further attacks.
In the information gathering stage, attackers try to gather information about the target database such as database name, version, users, output mechanism, DB type, user privilege level, and OS interaction level.
Once the information gathered, the attacker then tries to look for SQL vulnerabilities in the target web application. For that, he or she lists all input fields, hidden fields, and post requests on the website and then tries to inject codes into the input fields to generate an error.
The attacker then tries to carry out different types of SQL injection attacks such as error-based SQL injection, union-based SQL injection, blind (Wait for Delay) SQL injection, etc. Once the attacker succeeds in performing a SQL injection attack, he or she then tries to extract table names, column names, and table data from the target database. Depending upon the aim of the attacker, he or she may interact with the OS to extract OS details and application passwords, execute commands, access system files, etc. The attacker can go further to compromise the whole target network by installing Trojans and planting keyloggers.
9. Advance SQLI Injection
The attackers gain control by gathering information from errors generated.
Understanding the underlying SQL query will allow the attacker to craft correct SQL injection statements. Error messages are essential for extracting information from the database. Depending on the type of errors found, you can vary the attack techniques. Information gathering is also known as the survey and assess method used by the attacker to determine complete information of the potential target. Attackers find out what kind of database is used, what version is being used, user privilege levels, and various other things. The attacker usually gathers information at various levels starting with identification of the database type being used and the database search engine. Different databases require different SQL syntax. Identify the database engine used by the server. Identification of the privilege levels is one more step as there is chance of gaining the highest privilege as an authentic user. Then obtain the password and compromise the system. Interacting with the operating system through command shell execution allows you to compromise the entire network.
The attacker gains information through the error messages. The most common ones are.
Grouping Errors
Mismatch Errors
Blind Injection Errors
10. Bypass Website Logins Using SQL Injection
Attackers take complete advantage of vulnerabilities. SQL commands and user- provided parameters are chained together by programmers. By utilizing this feature, the attacker executes arbitrary SQL queries and commands on the backend database server through web applications.
Try the following SQL injection strings to bypass login scripts:
admin‘ – admin’ # admin’/* ‘ or 1=1—— ’ or 1=1# ’ or 1=1/* ') or ‘1’='1—- ') or (‘1’=‘1—
10.1 MD5 Hash Password
You can union resuits with a known password and MDS hash of a supplied password. The web application will compare your password and the supplied MDS hash instead of MD5 from the database.
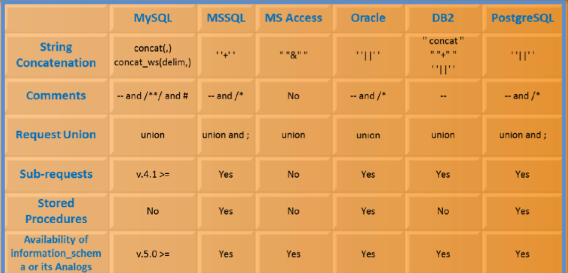
10.2 Features of different DBMS
11. SQL Injection Tools
NOTE: I am not putting any download links for security purpose. Just google these names and you will find them. Download at your own risk.
11.1 Recommended Tools
BSQL
Marathon Tool
SQL Power Injector
Havij
Other Tools
SQL Brute
Bobcat
SQLNinja
sqlget
Absinthe
Blind SQL Injection Bruteforcer
sqlmap
SQL Injection Digger
Pangolin
SQLPAT
F-J Injector Framework
Exploiter beta
SQLIer
Sqlsus
SQLInjector
SQL Inject-Me
NTO SQL Invader
The Mole
12. Evasion Techniques
12.1 Evading IDSs
Attackers use evasion techniques to obscure input strings in order to avoid detection by signature-based detection systems. Signature-based detection systems build a database of SQL injection attack strings (signatures) and then compare input strings against the signature database at runtime to detect attacks. If any information provided matches the attack signatures present in the database, then it immediately sets off an alarm. This kind of problem is more in network-based IDS systems (NlDSs) and also in signature-based NIDS systems. S0 attackers should be very careful and try to attack the system by bypassing the signature-based IDS. Attackers use evasion techniques to obscure input strings in order to avoid detection by signature-based detection systems.
12.2 Types of Signature Evasion Techniques
Sophisticated Matches: Uses alternative expression of "OR 1=1”.
Hex Coding: Uses hexadecimal encoding to represent a SQL query string.
Manipulating White Spaces: White space diversity is one of the signatures used to prevent SQL injection attacks. In this, a sequence of two or more expressions are separated by a white space for a simple reason. A single word SELECT may generate a lot of false positives. The expression UNION SELECT may generate a good signature. If the signature isn’t built properly, the signature is of no use and is highly prone to attacks.
In-line Comment: Obscures input strings by inserting in-line comments between SQL keywords.
Char Encoding: Uses built-in CHAR function to represent a character.
String Concatenation: Concatenates text to create SQL keyword using DB specific instructions.
Obfuscated Codes: Obfuscated code is a SQL statement that has been made difficult to understand.
13. How to Defend Against SQL Injection Attacks
Implementing consistent coding standards, minimizing privileges, and
firewalling the server help in defending against SQL injection attacks.
Minimizing Privileges : Developers generally neglect security aspects while creating a new application, and tend to leave those matters to the end of the development cycle. However, security matters should be a priority, and adequate steps must be incorporated during the development stage itself. it is important to create a low-privilege account first, and begin to add permissions only as they are needed. The benefit to addressing security early is that it allows developers to address security concerns as features are added, so they can be identified and fixed easily. In addition, developers become much more familiar with the security framework, if they are forced to comply with it throughout the project’s lifetime. The payoff is usually a more secure product that does not require the last minute security scramble that inevitably occurs when customers complain that their security policies do not allow applications to run outside of the system administrator’s context.
Implementing Consistent Coding Standards : Successful planning of the whole security infrastructure that would be integrated into a product should be carried out. Apart from this, a set of standards and policies with which every developer must comply should be laid down. Take, for example, a policy for performing data access. Developers are generally allowed to use whatever data access method they like. This usually results in a multitude of data access methods, each exhibiting unique security concerns. A more prudent policy would be to dictate certain guidelines that guarantee similarity in each developer’s routines. This consistency would greatly enhance both the maintainability and security of the product, provided the policy is sound. Another useful coding policy is to ensure that all input validation checks are performed on the server. Although it is sometimes a performance technique to carry out data entry validation on the client, since it minimizes round-trips to the server, it should not be assumed that the user is actually conforming to that validation when they post information. In the end, all input validation checks should occur on the server.
Firewalling the SQL Server : lt is a good idea to firewall the server so that only trusted clients can contact it—in most web environments, the only hosts that need to connect to SQL Server are the administrative network (if one is there) and the web server(s) that it services. Typically, SQL Server needs to connect only to a backup server. SQL Server 2000 listens by default on named pipes (using Microsoft networking on TCP ports 139 and 445) as well as TCP port 1433 and UDP port 1434 (the port used by the SQL "Slammer” worm). If the server lockdown is good enough, it should be able to help mitigate the risk of the following:
Developer uploading unauthorized/insecure scripts and components to the web server
Misapplied patches
Administrative errors
13.1 Word of Advice
Attackers use SQL injections to gain unauthorized access into the system or network. The following things should be done to defend against SQL injection attacks.
Make no assumptions about the size, type, or content of the data that is received by your application.
Test the size and data type of input and enforce appropriate limits to prevent buffer overruns.
Test the content of string variables and accept only expected values.
Reject entries that contain binary data, escape sequences, and comment characters.
Never build Transact-SQL statements directly from user input and use stored procedures to validate user input.
Implement multiple layers of validation and never concatenate user input that is not validated.
13.2 Final words
To defend against SQL injection attacks, you can follow the countermeasures stated in the previous section and you can use type-safe SQL parameters as well. To protect the web server, you can use WAF firewall/IDS and filter packets. You need to constantly update the software using patches to keep the server up-to-date to protect it from attackers. Sanitize and filter user input, analyze the source code for SQL Injection, and minimize the use of third-party applications to protect the web applications. You can also use stored procedures and parameter queries to retrieve data and disable verbose error messages, which can guide the attacker with some useful information, and use custom error pages to protect the web applications. To avoid SQL injection into the database, connect using non-privileged accounts and grant least privileges to the database, tables, and columns. Disable commands such as xp_“SEE”“M"dshe"ll”, which can affect the OS of the system.
14. SQL Injection Detection Tools
SQL Injection Detection tool from Microsoft
dotDefender
IBM Security Appscan
WebCruiser
HP WebInspect
SQLDict
HPScrawlr
SQL Block Monitor
Acunetix Web Vulnerability Scanner
GreenSQL Database Security
Microsoft Code Analysis Tool
NGS Squirrel Vulnerability Scanner
WASSA
N-Stalker
Enjoy!